| NBRP Rat No: 0469 |
Strain name: W-Tg(Gnrh1-EGFP)Nphy |
Commmon Name: Wistar-Tg(Gnrh1-EGFP)Nphy, Wistar-Tg(GnRH-EGFP)Nphy |
Rat Genome Database |
| Principal Investigator: |
Masakatsu Kato Nippon Medical school 1-1-5, Sendagi, Bunkyo-ku 113-8602 Tokyo Japan |
| Tel: 03-3822-2131 ext 5242 Fax: 03-5685-3055 |
Email: mkato@nms.ac.jp |
| Preservation Status: |
Embryo Sperm Living Animals |
 |
 |
| Coat Color |
albino (c) |
| Inbred Generations |
F?+13 (April 2012) |
| Usage Restrictions |
In publishing, a citation of the following literature(s) designated by the DEPOSITOR is requested. (see References) |
| Genetic Status |
|
| Comercial Availability |
|
|
| Research Category |
|
| Gene Affected |
GFP: Green Fluorescent Protein, jellyfish |
| Origin |
This trans genic strain was established in 2001. |
| Strain characteristics |
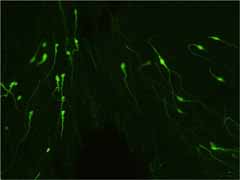
This transgenic strain contains the enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) gene driven by gonadotropin-releasing hormone 1 (Gnrh1) promoter. EGFP fluorescence is observed only in Gnrh1-immunoreactive neurons, approximately one third of which has strong EGFP fluorescence. |
| Breeding Conditions |
Since high inbred generations reduce breeding performance, crossing to wild type is necessary once in a while. |
| Genotyping |
Genotyping protocol for Gnrh1-EGFP
|
| References |
Kato M, Ui-Tei K, Watanabe M, Sakuma Y.
Characterization of voltage-gated calcium currents in gonadotropin-releasing hormone neurons tagged with green fluorescent protein in rats.
Endocrinology. 144(11):5118-25, 2003.
Yin C., Ishii H., Tanaka N., Sakuma Y., Kato M.
Activation of A-type g-amino butyric acid receptors (GABAARs) excites gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) neurones isolated from adult rats.
J Neuroendocrinol. 2008 May;20(5):566-75.
Kato M, Tanaka N, Usui S, Sakuma Y.
The SK channel blocker apamin inhibits slow afterhyperpolarization currents in rat gonadotropin-releasing hormone neurones.
J Physiol. 15;574(Pt 2):431-42, 2006.
Watanabe M., Sakuma Y., Kato M.
GABAA receptors mediated excitation in adult rat GnRH neurons.
Biol Reprod. 2009 Aug;81(2):327-332.
Kato M., Tanaka N., Ishii H., Yin C., Sakuma Y.
Ca2+ channels and Ca2+-activated K+ channels in adult rat gonadotrophin-releasing hormone neurones.
J Neuroendocrinol. 2009 Mar;21(4):312-315.
Tanaka N., Ishii H., Yin C., Koyama M., Sakuma Y., Kato M.
Voltage-gated Ca2+ channel mRNAs and T-type Ca2+ currents in rat gonadotropin-releasing hormone neurons.
J. Physiol. Sci. 2010 May;60(3):195-204.
Koyama M, Yin C, Ishii H, Sakuma Y, Kato M.
Somatostatin inhibition of GnRH neuronal activity and the morphological relationship between GnRH and somatostatin neurons in rats.
Endocrinology. 2012 Feb;153(2):806-814.
Tada H, Kuroki Y, Funabashi T, Kamiya Y, Goto T, Suyama K, Sano A, Mitsushima D, Etgen AM, Takahashi T.
Phasic synaptic incorporation of GluR2-lacking AMPA receptors at gonadotropin-releasing hormone neurons is involved in the generation of the luteinizing hormone surge in female rats.
Neuroscience. 2013 Sep 17;248:664-66 |
| Additional strain information |
|
|
|