| NBRP Rat No: 0042 |
Strain name: LEC/Hok |
Commmon Name: LEC, Long Evans Cinnamon |
Rat Genome Database |
| Principal Investigator: |
Kazuhiro Kitada Creative Research Initiative "Sousei", Hokkaido University Kita 10 Nishi 8, Kita-ku 060-0810 Hokkaido JAPAN |
| Tel: 011-706-3582 Fax: 011-726-3476 |
Email: kkitada@sci.hokudai.ac.jp |
| Preservation Status: |
Embryo Sperm Living Animals |
 |
 |
| Coat Color |
cinnamon-like (A,B,C,D,r) |
| Inbred Generations |
F107 (May 2009) |
| Usage Restrictions |
|
| Genetic Status |
|
| Comercial Availability |
|
|
| Research Category |
|
| Gene Affected |
Atp7b: ATPase, Cu++ transporting, beta polypeptide, Ptprk: protein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, K |
| Origin |
In 1975, at the Center for Experimental Plants and Animals, Hokkaido University, two inbred strains, LEC and LEA (NBRP No.0041), were established from a closed colony of Long-Evans rats obtained from Kobe University. In 1984, within the LEC rats of their F24 generation, a rat exhibiting spontaneous hepatitis with severe jaundice was found (Yoshida, 1987). (Jul 20, 2010) |
| Strain characteristics |
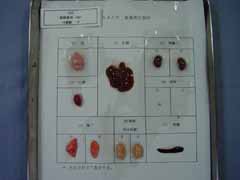
Hepatitis. Helper T-cells immunodeficiency. An animal model for human Wilson disease. High susceptibility to X-rays.
LEC rats develop spontaneous acute hepatitis with 40% mortality at about 4 months of age (Yoshida, 1987; Mori, 1994). Severe jaundice, subcutaneous bleeding, oliguria and loss of body weight are detected. The surviving rats develop to chronic hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma due to copper accumulation in the liver.
Backcross experiments demonstrated the hepatitis was caused by an autosomal recessive gene, hts (Yoshida, 1987; Masuda, 1988). At least 900-bp deletion of Atp7b gene, P-type copper transporting ATPase, was identified (Wu, 1994).
A deficiency in CD4+ T-cells in LEC rats was caused by an arrest of the maturation from CD4+8+ to CD4+ cells in the thymus (Yamada, 1991; Agui, 1990). This phenotype was caused by thid (T-helper immunodeficiency) and thid was identified as a genomic deletion of about 380-kb deletion that including the almost coding exons of Ptprk and the first exon of Themis (Asano, 2007; Kose, 2007; Iwata, 2010).
LEC rats are highly susceptible to X-irradiation (Hayashi, 1992). A strong QTL was mapped on Chr 4 (Agui, 2000). To identify radiation susceptibility genes, congenic LEC lines were developed and analyzed (Tsuji, 2005). (Jul 20, 2010) |
| Breeding Conditions |
Sib-mating, but approximately 40% mortality. |
| Genotyping |
|
| References |
Yoshida MC, Masuda R, Sasaki M, Takeichi N, Kobayashi H, Dempo K, Mori M.
New mutation causing hereditary hepatitis in the laboratory rat.
J Hered. 1987 Nov-Dec;78(6):361-5.
Mori M, Hattori A, Sawaki M, Tsuzuki N, Sawada N, Oyamada M, Sugawara N, Enomoto K.
The LEC rat: a model for human hepatitis, liver cancer, and much more.
Am J Pathol. 1994 Jan;144(1):200-4.
Masuda R, Yoshida MC, Sasaki M, Dempo K, Mori M.
Hereditary hepatitis of LEC rats is controlled by a single autosomal recessive gene.
Lab Anim. 1988 Apr;22(2):166-9.
Wu J, Forbes JR, Chen HS, Cox DW.
The LEC rat has a deletion in the copper transporting ATPase gene homologous to the Wilson disease gene.
Nat Genet. 1994 Aug;7(4):541-5.
Yamada T, Natori T, Izumi K, Sakai T, Agui T, Matsumoto K.
Inheritance of T helper immunodeficiency (thid) in LEC mutant rats.
Immunogenetics. 1991;33(3):216-9.
Agui T, Oka M, Yamada T, Sakai T, Izumi K, Ishida Y, Himeno K, Matsumoto K.
Maturational arrest from CD4+8+ to CD4+8- thymocytes in a mutant strain (LEC) of rat.
J Exp Med. 1990 Dec 1;172(6):1615-24.
Asano A, Tsubomatsu K, Jung CG, Sasaki N, Agui T.
A deletion mutation of the protein tyrosine phosphatase kappa (Ptprk) gene is responsible for T-helper immunodeficiency (thid) in the LEC rat.
Mamm Genome. 2007 Nov;18(11):779-86.
Kose H, Sakai T, Tsukumo S, Wei K, Yamada T, Yasutomo K, Matsumoto K.
Maturational arrest of thymocyte development is caused by a deletion in the receptor-like protein tyrosine phosphatase kappa gene in LEC rats.
Genomics. 2007 Jun;89(6):673-7.
Iwata R, Sasaki N, Agui T.
Contiguous gene deletion of Ptprk and Themis causes T-helper immunodeficiency (thid) in the LEC rat.
Biomed Res. 2010;31(1):83-7.
Agui T, Miyamoto T, Jung CG, Tsumagari T, Masuda K, Manabe T.
Genetic linkage analysis of X-ray hypersensitivity in the LEC mutant rat.
Mamm Genome. 2000 Oct;11(10):862-5.
Tsuji AB, Sugyo A, Ogiu T, Sagara M, Kimura T, Ishikawa A, Sudo H, Ohtsuki M, Aburatani H, Imai T, Harada YN.
Fine mapping of radiation susceptibility and gene expression analysis of LEC congenic rat lines.
Genomics. 2005 Sep;86(3):271-9. |
| Additional strain information |
LEC |
|
|